Before we can initiate any packet sniffing operations or even discovering networks we have to first change the wireless mode from “managed” to “monitor.” This is a very easy procedure which is given below.
Changing Wireless Modes

Discovering Nearby Networks

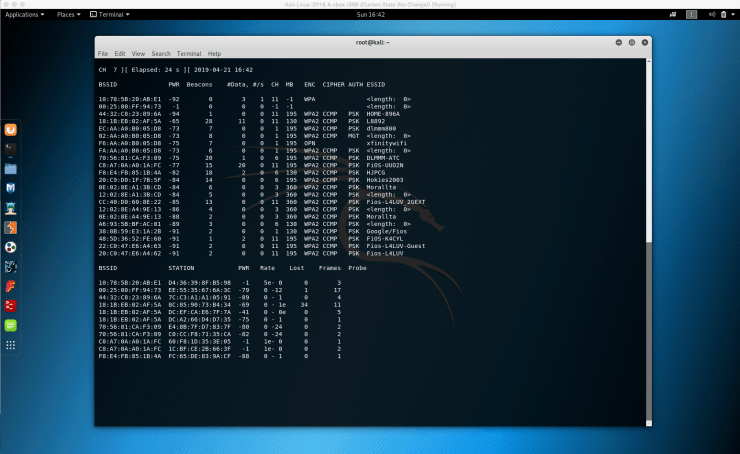
I want to explain the various pieces of information we’re being shown. These are all critical pieces of information we need to be able to read before we can delve deeper into more advanced procedures.
ESSID: This should seem familiar. We can see all the networks that are in range. This will become more useful for later operations.
BSSID: This shows the MAC address of the target network.
PwR: This is the signal strength or power of the network. The higher the number, the better the signal.
Beacons: These are frames sent by the network in order to broadcast its existence. Every network, even hidden always sends these type of frames.
#Data: This is the number of data packets or data frames. These are the useful packets that will be more useful in actual cracking.
#/S: Represents the number of data packets collected in the last 10 seconds.
CH: This is the channel which the network works on.
MB: MB is the maximum speed supported by the network.
ENC: This is the encryption and this is very important. We find out the encryption method being used by the network.
CIPHER: This is showing the cipher being used in the network.
AUTH: This is the authentication used on the network. PSK indicates pre-shared key.
